Leaf Anatomy
For example Hartikainen et al. Typically a leaf consists of a broad expanded blade the lamina attached to the plant stem by a stalklike petiole.
 Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Botany Anatomy Leaves
Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Botany Anatomy Leaves
What Are the Main Parts of a Leaf.

Leaf anatomy. Leaves are responsible for converting sunlight and carbon dioxide into glucose which is used to provide energy to the plant. How Is A Leaf Organized. The leaf both morphologically and anatomically is the most variable plant organ.
On top of the leaf is a waxy noncellular layer called the cuticle. The leaves and stem together form the shoot. Leaves are the primary food producing organs of a plant They are designed to efficiently collect light and use that light energy to produce food Remember that this process is called photosynthesis There are several parts of a leaf.
The cuticle is on the leaf. In the present chapter common features of leaf anatomy are described and the current knowledge related to its functions is summarized. It grows in many environments but tends to prefer shaded cool spots with plenty of moisture.
Structures within a leaf convert the energy in sunlight into chemical energy that the plant can use as food. Leaf anatomy in C4 plants. This small herbaceous flowering plant is more commonly referred to as a buttercup.
In angiosperms leaves commonly have a pair of structures known as stipules which are located on each side of the leaf base and may resemble scales spines glands or leaflike structures. They have been grouped as foliage leaves cataphylls hypsophylls and cotyledons. The lamina has two faces the upper face or the dorsal face or the adaxial surface is deep green in color due to the presence of more density of chlorophyll while the lower surface or the ventral surface or the abaxial surface is grass-green in color due.
Leaves are food factories for the tree. Zabel examines the anatomy of a leaf and chloroplast. These tissues include a mesophyll tissue layer that is sandwiched between two layers of epidermis.
Outer mesophyll cells and inner spongy bundle sheath cells arranged in a circular manner like a necklace thus leaves of C 4 plants contain two types of chloroplast viz. A few plants have a spreading vein pattern called dichotomous venation. Cuticle on top of the leaf is a waxy non-cellular layer Prevents water from escaping the leaf It is usually very thick on plants in arid regions.
A leaf plural leaves is the principal lateral appendage of the vascular plant stem usually borne above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. In most plants leaves are the major site of food production for the plant. In anatomy of leaf it is clear that the lateral sides of the lamina form the leaf margin.
It consists of a flattened portion called the blade that is attached to the plant by a structure called the petiole. The C4 biochemical pathway relies on a specific suite of leaf functional properties often referred to as Kranz anatomy. Leaves are however quite diverse in size shape and various other characteristics including the nature of the blade margin and the type of venation arrangement of veins.
Sometimes leaves are divided into two or more sections called leaflets. Anatomy of the leaf is the detailed study of the internal structure of a leaf usually revealed by its dissection. Of these the foliage leaves are the principal photosynthetic organs.
It is a good example of a standard leaf not specially adapted to either wet or dry environments. Leaves can be found in a variety of shapes and sizes. The leaf is the primary photosynthetic organ of the plant.
The cataphylls are the scales that appear on the buds and on underground stem for their protection. A leaf is organized to collect sunlight and turn it through photosynthesis into food The leaf has many layers of tissue to allow this to happen. Basic Leaf Anatomy of Flowering Plants.
Predict the drought tolerance of a leaf using anatomical and morphological features. Identify tissues and structures within a variety of leaves. View a prepared slide of a Ranunculus leaf.
These include the existence of discrete compartments differentially connected to the atmosphere a close contact between these compartments and a relatively large compartment to host the Calvin cycle. In this Biology lesson Mr. Leaf shape is adapted to best suit the plants habitat and maximize photosynthesis.
The leaf blade is constructed of many layers that make this happen. Identify whether a leaf is mesophytic xerophytic or hydrophytic based on leaf anatomy. Special emphasis will be given to leaf optical properties gas diffusion water transport and mechanical properties.
The hyposophylls are the various. Leaves are classified into mainly two types based on their structure dorsiventral and isobilateral. LEAF ORGANIZATION A leaf is organized to collect sunlight.
Leaves are collectively referred to as foliage as in autumn foliage. Showed no alterations of leaf anatomy to long-term warming 11 20. Found that leaf anatomy can respond sensitively to short-term warming but Schollert et al.
Mesophyll chloroplast and bundle sheath chloroplast ie. Chlorophyll is the molecule in leaves that uses the energy in sunlight to turn water H 2 O and carbon dioxide gas CO 2 into sugar and oxygen gas O 2. Use the process of science to ask and answer scientific questions.
Powered by sunlight the green substance in leaves called chlorophyll use carbon dioxide and water to produce life-sustaining carbohydrates sugars. Some plants such as conifers have leaves that are shaped like needles or scales. The alterations in leaf anatomy can then affect photosynthetic gas exchange.
Leaf anatomy showed acclimation to long-term warming. Leaf anatomy the leaf is the primary photosynthetic organ of the plant. Most leaves are broad flat and typically green in color.
Leaves of C 4 plants show two type of cells viz. A gingko leaf has veins of this type.
 English Leaf Anatomy Legend 1 Cuticle 2 Upper Epidermis 3 Palisade Mesophyll 4 Spongy Mesophyll 5 Lower Epide Vascular Plant Plant Structure Cell Model
English Leaf Anatomy Legend 1 Cuticle 2 Upper Epidermis 3 Palisade Mesophyll 4 Spongy Mesophyll 5 Lower Epide Vascular Plant Plant Structure Cell Model
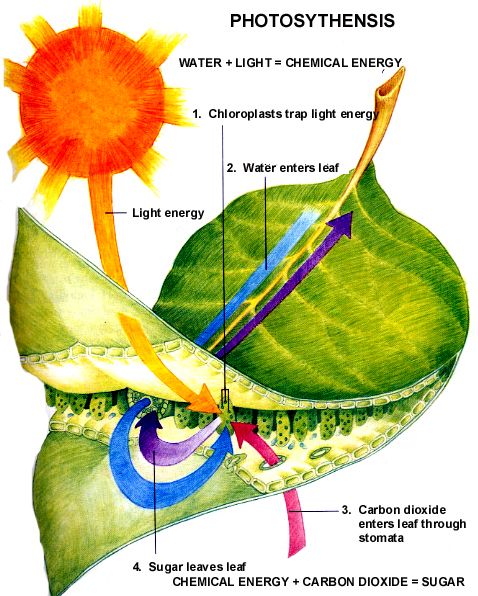 Let S Learn Photosynthesis Leaf Anatomy Pendidikan Eksperimen Sains Biologi
Let S Learn Photosynthesis Leaf Anatomy Pendidikan Eksperimen Sains Biologi
 Inside A Green Leaf Flower Structure Plant Leaves Science Images
Inside A Green Leaf Flower Structure Plant Leaves Science Images
 Pine Leaf Needle Anatomy Stock Illustration Illustration Of Green 51040841 Pine Leaf Botany Lessons Needle
Pine Leaf Needle Anatomy Stock Illustration Illustration Of Green 51040841 Pine Leaf Botany Lessons Needle
 Leaf Anatomy Coloring Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Teacher
Leaf Anatomy Coloring Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Teacher
 Plant Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Plant Leaves Leaves Plants
Plant Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Plant Leaves Leaves Plants
 Leaf Anatomy Coloring Anatomy Color Coloring Pages
Leaf Anatomy Coloring Anatomy Color Coloring Pages
 Leaf Anatomy Project What Makes A Leaf Leaf Structure And Function Leaf Structure Image
Leaf Anatomy Project What Makes A Leaf Leaf Structure And Function Leaf Structure Image
 Leaf Anatomy Vector Illustration Diagram Plant Science Anatomy Biology Lessons
Leaf Anatomy Vector Illustration Diagram Plant Science Anatomy Biology Lessons
 Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Enchantedlearning Com Leaf Structure Photosynthesis Plant Science
Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Enchantedlearning Com Leaf Structure Photosynthesis Plant Science
 Parts Of A Flower And Plant Do You Know Them All 7 Diagrams Flower Cell Leaf Stem Etc Microscopic Photography Photosynthesis Parts Of A Flower
Parts Of A Flower And Plant Do You Know Them All 7 Diagrams Flower Cell Leaf Stem Etc Microscopic Photography Photosynthesis Parts Of A Flower
 Leaf Anatomy Diagram On A White Background Ad Spon Anatomy Leaf Diagram Background Palisade Cell Epidermis Website Template
Leaf Anatomy Diagram On A White Background Ad Spon Anatomy Leaf Diagram Background Palisade Cell Epidermis Website Template
 Pin On Plant Structure And Function For Students
Pin On Plant Structure And Function For Students
 Anatomy Leaf Projects Plant Leaves Anatomy
Anatomy Leaf Projects Plant Leaves Anatomy
 Leaf Anatomy Coloring Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Teacher
Leaf Anatomy Coloring Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Teacher
 Plant Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Plant Leaves Plant Tissue Anatomy
Plant Leaves And Leaf Anatomy Plant Leaves Plant Tissue Anatomy
 Leaf Sructure Plant Structure Leaf Structure Structure And Function
Leaf Sructure Plant Structure Leaf Structure Structure And Function
 Leaf Anatomy Illustration Of A Leaf Anatomy On A White Background Ad Illustration Anatomy Leaf B Photosynthesis Creative Poster Design Illustration
Leaf Anatomy Illustration Of A Leaf Anatomy On A White Background Ad Illustration Anatomy Leaf B Photosynthesis Creative Poster Design Illustration
 Plant Stem Structure Model Google Zoeken Plant Science Botany Plant Structure
Plant Stem Structure Model Google Zoeken Plant Science Botany Plant Structure
Post a Comment for "Leaf Anatomy"