Figure 9-3 Anatomy Of The Eye Answers
View of the human eye. Figures 91 93 97 99 and 910 NA Forms the forehead superior part of the orbit and the floor of the anterior cranial fossa.
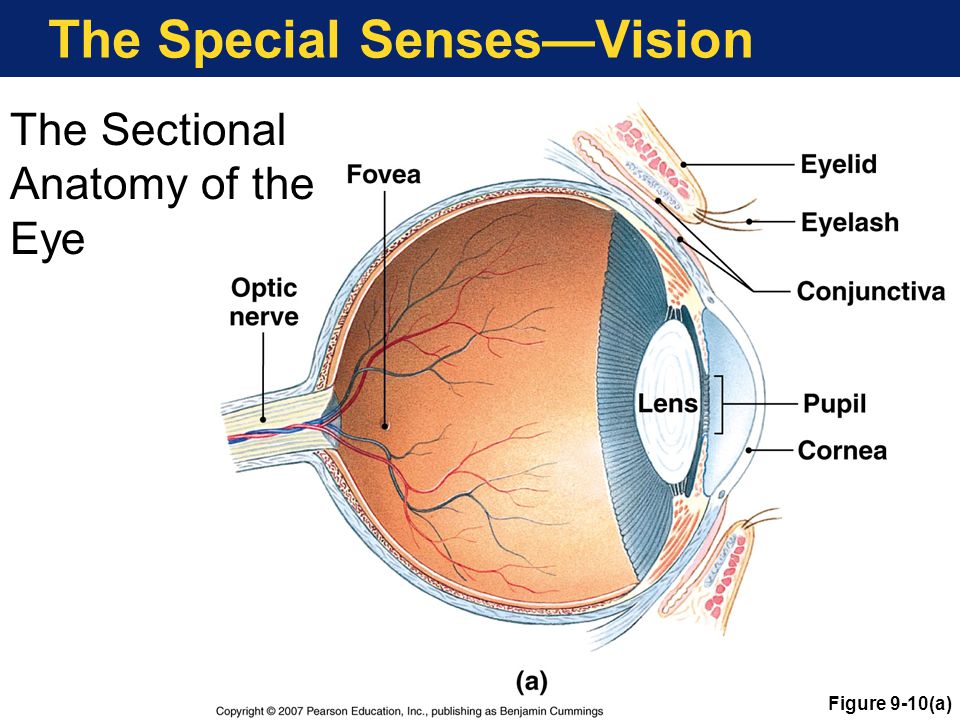
The sclera accounts for five sixths of the surface of the eye most of which is not visible though humans are unique compared with many other species in having so much of the white of the eye visible Figure 3.

Figure 9-3 anatomy of the eye answers. 5 - the axial skeleton. The iris constricts the pupil in response to bright light and dilates the pupil in response to dim light. A black-looking aperture the pupilthat allows light to enter the eye it appears dark because of the absorbing pigments in the retina.
The tears flow downward and medially across the eye. Expert Answer a cornea 7 - slightly projected transparent anterior part of the sclera which refracts light rays to focus on the retina. The lacrimal apparatus consists of the lacrimal gland which secretes tears and a series of ducts that carry tears into the nasal cavity Figure 3.
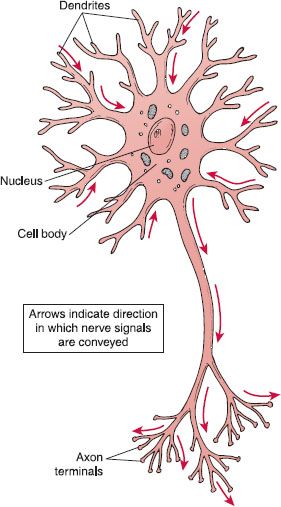
3 - the cell. Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within central nervous system. Nerve fiber arising from a slight elevation of the cell body that conducts an impulse action potential away from the cell body.
The innermost layer of the eye is the neural tunic or retina which contains the nervous tissue responsible for photoreception. Rogers Revised Lab Final - Study Guide Exam 1 Review - Lecture notes Exam 1 Essentials of Pathophysiology - Exam 2 review sheet Test 2 Essay 4 - Grade. The back part of the eyes interior.
The light-sensitive nerve layer that lines the inside of the back of the eye. Lec Sum 1 Ch10 Thermochemistry Lec Sum 8 Naming Ionic compounds Ch 1 psychopathology - Lecture notes 1-2 Exam 1 Study Guide College Writing Paper Two ENGL1020262. Supraorbital foramen notch Opening above each orbit allowing blood vessels and nerves to pass.
Learn the anatomy of a typical human cell. The cornea the front transparent layer of the eye and the crystalline lens a transparent convex structure behind the cornea both refract bend light to focus the image on the retina. Scleral venous sinus The ________________ canal of Schlemm is an opening found at the junction of the cornea and the sclera.
2025 Assignment 18 - Homework 18 from Mechanics of Materials 7th Edition. Star-shaped neuroglia between neurons and blood vessels. Select One Anterior Chamber Ciliary Body Cornea Fibrous Tunic Iris Lateral Rectus Muscle Lens Medial Rectus Muscle Optic Disk Optic Nerve Pupil Retina Vascular Tunic Vitreous Nerve.
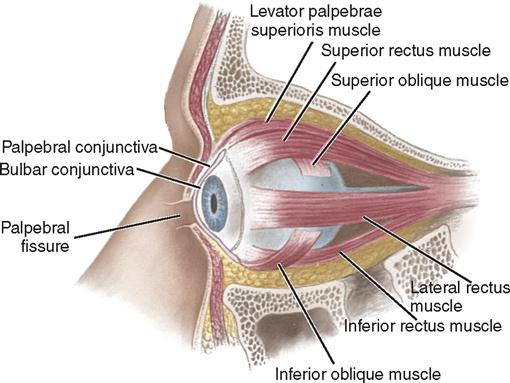
Describe the external internal anatomical structures of the human eye. Answer to Tectus oblique oblic de Dw muscle muscle Will Identifying Accessory Eye Structures Using a chart of eye anatomy or Figu. 7 - the muscles.
The anterior cavity and the posterior cavity. Explain how the sphincter pupillae the dilator pupillae muscles work together to control the amount of light that is admitted to the eye. 1 Photoreceptor 2 Retina cell 3 Bipolar cell 4 Ganglion cell 5 Optic nerve cell.
A colored circular muscle the iris which is beautifully pigmented giving us our eyes color the central aperture of the iris is the pupil Fig. The retina senses light and creates impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain. The eye protects itself using eyelids eyelashes and tears.
If somebody is nearsighted it means that they have trouble seeing things far away. The retina or nervous tunic is the innermost tunic and it covers the posterior five-sixths of the eye. With each blink a small amount of tears is released onto the eye to wash away dust and bacteria.
Do you know the bones of the skull. View the full answer. The opening in the middle of the iris through which light passes to the back of the eye.
The eye is also divided into two cavities. Label Parts of the Human Eye. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education Inc.
Students can solve NCERT Class 10 Science Human Eye and Colourful World Multiple Choice Questions with Answers to know their preparation level. Figure 157 Part of the posterior wall fundus of the right eye as seen with an ophthalmoscope. The least distance of distinct vision for a normal eye is a infinity b 25 cm c 25 cm d 25 m.
The iris which is conspicuous as the colored part of the eye is a circular muscular ring lying between the lens and cornea that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. Supraorbital margin Thick margin of the eye socket that lies beneath the eyebrows. This circular muscle controls the size of the pupil so that more or less light depending on conditions is allowed to enter the eye.
How about the bones of the axial skeleton. Identify the anatomical structures associated with the retina explain how they work together to produce vision. Eyelids blink to help keep things out of the eye and also to keep the eye moist.
The transparent cornea covers the anterior tip of the eye and allows light to enter the eye. Macula lutea Central artery and vein emerging from the optic disc Optic disc Retina. 6 - the heart.
Can you identify the muscles of the body. Anatomy-Eye Picturesdocx - 3 a 9553 a 2 s 53 SE a Figure 93 m EIIIIHEII Eye Muscles Hall ID5II Emnmh Ilka-slums Levat-er SuperI-er palpeh rse. Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World.
The _____ scler- hard is the tough white part of the eye that forms the majority of the eyeball. It is the innermost tunic and it covers the posterior five-sixths of the eye. 4 - the skull.
It consists of an outer pigmented retina and an inner sensory retina. Name the parts of the human heart. The lacrimal gland is located in the orbit and secretes tears continuously through tiny tubules.
 The Human Body Structure And Function Basicmedical Key
The Human Body Structure And Function Basicmedical Key
 Image Result For Cool Maths Stuff Fun Math Math Quotes And Notes
Image Result For Cool Maths Stuff Fun Math Math Quotes And Notes
 Chapter 9 Body Organization Ppt Download
Chapter 9 Body Organization Ppt Download
 Eye Anatomy Nose Pores Ciliary Muscle Rectus Muscle
Eye Anatomy Nose Pores Ciliary Muscle Rectus Muscle
 3 4 View Skeleton Neanderthal Human Skeleton Anatomy Animal Skeletons
3 4 View Skeleton Neanderthal Human Skeleton Anatomy Animal Skeletons
 Internal Anatomy Of The Eye Anatomy Drawing Diagram
Internal Anatomy Of The Eye Anatomy Drawing Diagram
 The Skeletal System The Bones Of The Full Skeleton From The Side Human Body Systems Arm Bones Bones Of The Head
The Skeletal System The Bones Of The Full Skeleton From The Side Human Body Systems Arm Bones Bones Of The Head
 The General Senses Sensory Basics Ppt Video Online Download
The General Senses Sensory Basics Ppt Video Online Download
 Daily Sketches Portfolio Work And Other Art Things Art Assignments Drawing People Art Tutorials
Daily Sketches Portfolio Work And Other Art Things Art Assignments Drawing People Art Tutorials
 Printable Human Skeleton Diagram Labeled Unlabeled And Blank Human Skeleton Model Human Skeleton Labeled Human Skeleton
Printable Human Skeleton Diagram Labeled Unlabeled And Blank Human Skeleton Model Human Skeleton Labeled Human Skeleton
 9 Ophthalmic Surgery Basicmedical Key
9 Ophthalmic Surgery Basicmedical Key
 L 6 The Eye 1 Purpose To Investigate The Eye Considered As An Optical Instrument Several Specific Measurement Tasks Include 1 Measurement Of The Pupil Size In The Dark And Bright Adapted Eye 2 Measurement Of The Time Delay Of Visual Signals
L 6 The Eye 1 Purpose To Investigate The Eye Considered As An Optical Instrument Several Specific Measurement Tasks Include 1 Measurement Of The Pupil Size In The Dark And Bright Adapted Eye 2 Measurement Of The Time Delay Of Visual Signals
 Chapter 9 11 Review Ppt Download
Chapter 9 11 Review Ppt Download
 Upside Down Plates Illusions Brain Images Plates
Upside Down Plates Illusions Brain Images Plates
 Sphenoid Bone Of The Human Skull Clipart Etc Sphenoid Bone Human Skull Bone Tattoos
Sphenoid Bone Of The Human Skull Clipart Etc Sphenoid Bone Human Skull Bone Tattoos
Https Isaacnewtonacademy Org Sites Default Files Biology 20paper 202 20foundation 20test Pdf
 Pin On Clinical State Of Depression
Pin On Clinical State Of Depression


Post a Comment for "Figure 9-3 Anatomy Of The Eye Answers"